The loan waiver year of 2008 saw 16,196 farm suicides in the country, according to the National Crime Records Bureau. Compared to 2007, that's a fall of just 436. As economist Professor K Nagaraj who has worked in-depth on farm suicide data says, "the numbers leave little room for comfort and none at all for self-congratulation." There were no major changes in the trend that set in from the late 1990s and worsened after 2002. The dismal truth is that very high numbers of farm suicides still occur within a fast decreasing farm population.
Between just the Census of 1991 and that of 2001, nearly 8 million cultivators quit farming. A year from now, the 2011 Census will tell us how many more quit in this decade. It is not likely to be less. It could even dwarf that 8 million figure as the exodus from farming probably intensified after 2001. The State-wise farm suicide ratios - number of farmers committing suicide per 100,000 farmers - are still pegged on the outdated 2001 figures. So the 2011 Census, with more authentic counts of how many farmers there really are, might provide an unhappy update on what is going on.
Focussing on farm suicides as a share of total suicides in India misleads. That way, it's "aha! the percentage is coming down." That's silly. For one thing, the total number of suicides (all groups, not just farmers) is increasing - in a growing population. Farm suicides are rising within a declining farm population. Two, an all-India picture disguises the intensity. The devastation lies in the Big 5 States (Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh). These account for two-thirds of all farm suicides during 2003-08. Take just the Big 5 - their percentage of all farm suicides has gone up. Worse, even their percentage of total all-India suicides (all categories) has risen. Poor States like Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh are doing very badly for some years now.
In the period 1997-2002, farm suicides in the Big 5 States accounted for roughly one out of every 12 of all suicides in the country. In 2003-08, they accounted for nearly one out of every 10.
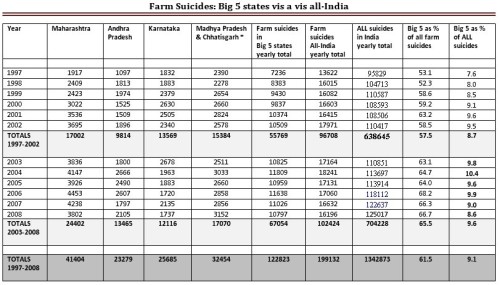
Farm suicides: The Big 5 states vis-a-vis all-India. MP & Chhattisgarh now have separately recorded data for recent years (available on the NCRB website). Since the
data for earlier years cannot be disaggregated we treat them as a single entity in this table.
Source: Data for 1997-2005 derived by Prof. K. Nagaraj from NCRB reports (Accidental Deaths & Suicides in India) for those years and extended thereafter with NCRB ADSI data from years 2006, 2007 and 2008.
The NCRB now has farm suicide data for 12 years. Actually, farm data appear in its records from 1995 onwards, but some States failed to report for the first two years. Hence 1997, from when all States are reporting their farm suicide data, is a more reliable base year. The NCRB has also made access much easier by placing all past years of Accidental Deaths & Suicides in India reports on its website.
The 12-year period allows us to compare farm suicide numbers for 1997-2002, with how they turned out in the next 6-year period of 2003-2008. All 12 years were pretty bad, but the latter six were decidedly worse.

In all, the amounts committed to fighting the agrarian crisis in Maharashtra exceeded Rs.20,000 crores across 2006, 2007 and 2008. Yet, that proved to be the worst three-year period ever for any State at any time since the recording of farm data began.

•
The dull days of White Gold
•
Over 16,000 suicides in 2007
•
Nearly 2 lakh suicides
In all, the amounts committed to fighting the agrarian crisis in Maharashtra exceeded Rs.20,000 crores across 2006, 2007 and 2008. (And that's not counting huge handouts to the sugar barons.) Yet, that proved to be the worst three-year period ever for any State at any time since the recording of farm data began. In 2006-08, Maharashtra saw 12,493 farm suicides. That is nearly 600 more than the previous worst of 2002-2005 and 85 per cent higher than the 6745 suicides recorded in the three-year period of 1997-1999. The same government was in power, incidentally, in the worst six years. Besides, these higher numbers are emerging within a shrinking farm population. By 2001, 42 per cent of Maharashtra's population was already urban. Its farmer base has certainly not grown.
So was the loan waiver useless? The idea of a waiver was not a bad thing. And it was right to intervene. More that the specific actions were misguided and bungled. Yet it could also be argued that but for the relief the waiver brought to some farmers at least, the suicide numbers of 2008 could have been a lot worse. The waiver was a welcome step for farmers, but its architecture was flawed. A point strongly made in this journal (see Oh! What a lovely waiver). It dealt only with bank credit and ignored moneylender debt. So only those farmers with access to institutional credit would benefit. Tenant farmers in Andhra Pradesh and poor farmers in Vidharbha and elsewhere get their loans mainly from moneylenders. So, in fact, farmers in Kerala, where everyone has a bank account, were more likely to gain. (Kerala was also the one State to address the issue of moneylender debt.)
The 2008 waiver also excluded those holding over five acres, making no distinction between irrigated and unirrigated land. This devastated many struggling farmers with eight or 10 acres of poor, dry land. On the other hand, West Bengal's farmers, giant numbers of small holders below the 5-acre limit, stood to gain far more.
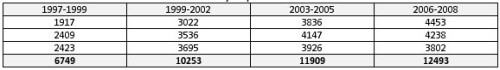
Farm suicides Maharashtra: four 3-year periods.
Every suicide has a multiplicity of causes. But when you have nearly 200,000 of them, it makes sense to seek broad common factors within that group. Within those reasons. As Dr. Nagaraj has repeatedly pointed out, the suicides appear concentrated in regions of high commercialisation of agriculture and very high peasant debt. Cash crop farmers seemed far more vulnerable to suicide than those growing food crops.
Yet the basic underlying causes of the crisis remained untouched. The predatory commercialisation of the countryside; a massive decline in investment in agriculture; the withdrawal of bank credit at a time of soaring input prices; the crash in farm incomes combined with an explosion of cultivation costs; the shifting of millions from food crop to cash crop cultivation with all its risks; the corporate hijack of every major sector of agriculture including, and especially, seed; growing water stress and moves towards privatisation of that resource. The government was trying to beat the crisis - leaving in place all its causes - with a one-off waiver.
In late 2007, The Hindu carried (Nov. 12-15) the sorry result emerging from Dr. Nagaraj's study of NCRB data: that nearly 1.5 lakh peasants had ended their lives in despair between 1997 and 2005. Just days later, Union Minister for Agriculture Sharad Pawar confirmed those figures in Parliament (Rajya Sabha Starred Question No. 238, Nov. 30, 2007) citing the same NCRB data. It's tragic that 27 months later, the paper had to run a headline saying that the number had climbed to nearly 2 lakh. The crisis is very much with us. Mocking its victims, heckling its critics. And cosmetic changes won't make it go away.